Share this article
Digital dental workflow Are you up for it?
Medical
The integration of digital dental workflow in dental practices represents a major paradigm shift in dentistry. One of the ongoing challenges is the collaboration between dentists and dental laboratories, and the management of impressions, whether they are conventional or digital.
In France, there are over 42,000 dentists. According to the XERFI study conducted in 2016, the number of digitally-equipped dental practices continues to increase (nearly 12% of practices), as well as the number of dental labs using digital workflows.
In this article, we will present the benefits of digital workflow in dentistry, which is a crucial tool for communication between the patient and the dentist, as well as a facilitator for data transmission with dental laboratories.
Want to learn more? Get in touch with us or our experts.

What does the commonly used term”digital dental workflow”really mean?
Digital workflow is an integral part of modern dentistry. It encompasses all digital processes that simplify complex therapies by digitizing all necessary information for exchange among all stakeholders in the dental industry.
Here are the different stages of digital workflow:
- Digital dental impression:The dentist uses an intraoral scanner to take an impression of the patient’s jaw. If necessary, the dentist makes a conventional impression with a plaster mold that is sent to the dental laboratory. The laboratory then digitizes the plaster model to retrieve digital data.
- 3D printing of dental prostheses: Using a 3D printer, this manufacturing technique is based on additive manufacturing. It involves adding material to produce precise prosthetic pieces designed by Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAD/CAM).
- Direct vs indirect dental CAD/CAM: Direct CAD/CAM refers to when the entire digital chain is directly integrated into the dental practice. Prosthetic elements are designed and fabricated in a single session, without going through the dental laboratory. Indirect CAD/CAM involves a conventional impression, which is sent to the laboratory to obtain digital data. There is also semi-direct CAD/CAM, which involves sending an STL file to the laboratory or a milling center.
- Validation by the practitioner
- Milling: The dental technician imports the digital file of the dental prosthesis into a CAD/CAM software. These digital data are sent to the milling machine to remove material to give the raw prosthetic piece the desired shape.
- Placement of the dental prosthesis by the dentist.

5 reasons to convince you to integrate digital workflow in your dental practice
The advent of digital technology is changing the way dental practices and dental labs operate. It is evident that switching to digital workflows offers considerable advantages for both the practitioner and the patient.
From the perspective of the dentist:
- Time-saving: digital dental impressions streamline the transmission of information to dental technicians. There is a significant increase in productivity with a reduction in material and postage costs, as well as an increase in patient care.
- Increased precision: the digital workflow is part of a learning curve that allows for more precise treatment protocols as they are used more frequently.
- More preventive and less invasive care: some software integrates with intraoral scanners, which can improve diagnosis accuracy, especially in detecting cavities and occlusion problems.
From the patient’s perspective:
- Easier acceptance of the treatment plan: patients can better visualize the different stages of treatment and understand the treatment plan.
- A genuine communication tool: a digital practice is more attractive to patients and builds trust.
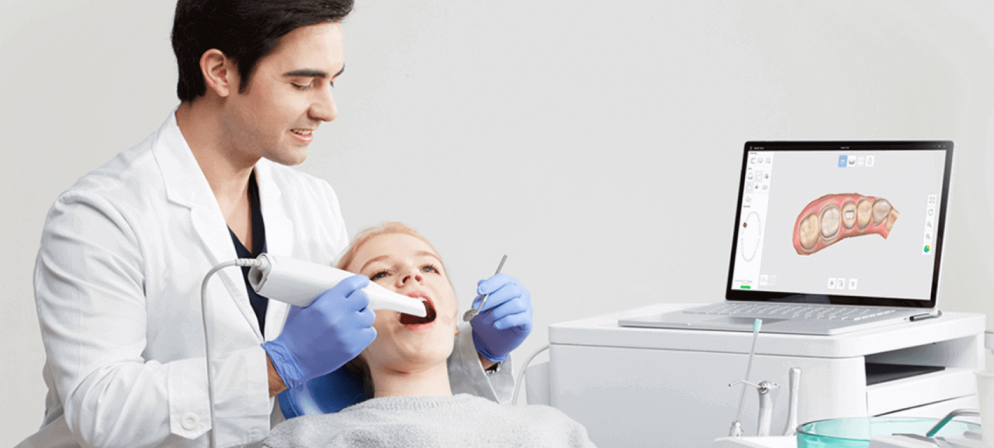
How to choose a dental intraoral scanner?
The intraoral scanner is one of the key elements of the digital workflow. Nowadays, there are numerous actors in the market, making it essential to know the selection criteria to consider when making your decision.
Here are some of them:
The size and weight of the scanner are essential indicators as you will be using it for many hours in your day. It is therefore recommended to choose an intraoral scanner whose weight does not exceed 350g. The lighter your camera, the easier it will be to handle.
Additional Features depend on the selected brand, you can obtain additional services, the most well-known of which are:
- Cavity detection, which can be performed using fluorescence or transillumination
- Occlusion detection
- Wired or wireless
- With or without a touch screen
- With CAD integration, in which case you will need to export the files and the prostheses will be designed using another software.
These additional features can add value to your practice and facilitate digital workflow. Moreover, the intraoral scanner is the first link in the digital chain, making it a crucial element in the process.
Scanning speed
This is considered one of the most important criteria to consider. New technologies have improved the scanning of the complete arch. Scanning speeds can vary from 30 seconds to several minutes.
Scanning flow
The intraoral scanner must take into account every angle of the semi-arches with a quick recovery of missing scans. This means the tool’s efficiency is important.
Price
This is one of the most important criteria for dentists. Indeed, depending on the brand and distributor, prices can vary for the same model. It is necessary to obtain several quotes and compare the different possible configurations according to the needs of the dental office.
The digitalization of dental offices offers many advantages. In addition to making your practice more attractive, you will attract more patients and increase your volume of clinical procedures. Modern dentistry is therefore constantly evolving.
Want to learn more? Get in touch with us or our experts.
Discover more
-
Bureau d’études
Reverse Engineering for Historical Object Preservation
Preserving historical objects is essential for transmitting culture and history to future generations.
Read more
-
History
Additive Manufacturing: Definition, Process, Advantages, and Applications
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, has rapidly become a technological revolution in industrial production.
Read more
-
Customer Interview
Synergy and Precision: The Partnership of Crown Ceram and Prodways Group Shapes the Future of Dental 3D Printing
At the Formnext trade show, overshadowed by various innovations, the teams from Prodways Group and Frédéric Rapp, CEO of the renowned Crown Ceram Laboratory, reflected on a collaboration that has stood the test of time.
Read more




